How a Project Management Office (PMO) Can Be an Engine of Innovation
Author: Hajime Estanislao, PMP®; Editor: Geram Lompon; Reviewed by: Alvin Villanueva, PMP®, PMI-ACP®
Projects are becoming interconnected, timelines are less predictable, and expectations are higher. Amid these challenges, organizations struggle to develop innovative ideas into results.
It is where a
Imagine an organization that regularly identifies opportunities to test new concepts and brings working solutions into practice while supporting operations. A PMO that supports innovation makes this possible by aligning creative exploration with strategic priorities. The PMO ensures innovation initiatives are consistent with the organization’s strategy, maintaining strategic coherence across business units.
This article discusses how PMOs can support innovation, the steps involved, and practical ways to embed innovation into project systems without sacrificing structure or accountability. Leadership support is essential for enabling the PMO to drive innovation and secure the necessary resources for success.

What is a Project Management Office (PMO)?
A
The PMO provides tools, templates, and shared standards that support planning and reporting. It monitors progress, connects departments, and helps project managers understand where projects stand and how they contribute to broader priorities. The PMO also plays a role in project governance, ensuring projects adhere to organizational standards and decision-making processes. Some PMOs offer support and guidance; others have more direct authority and oversight.
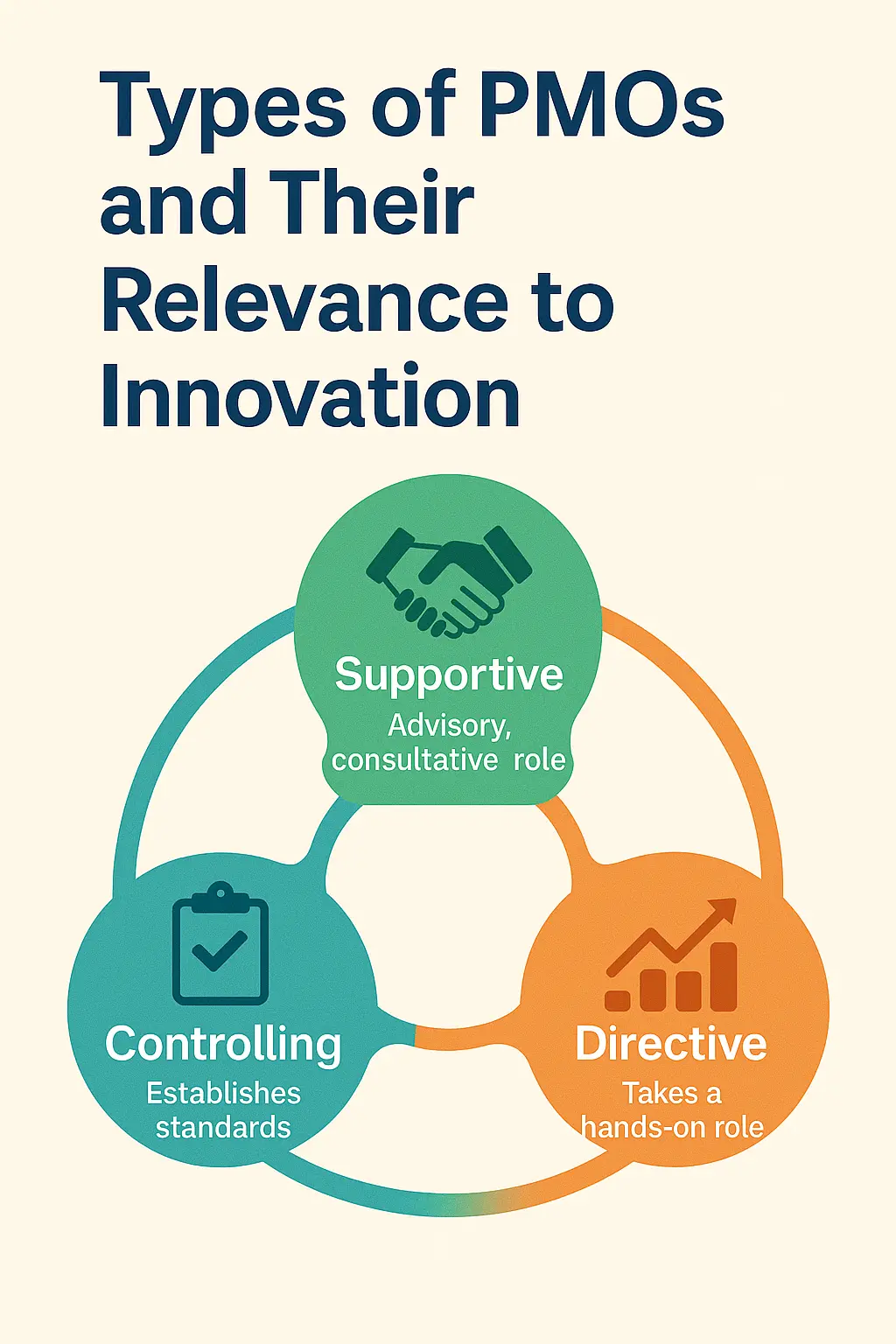
Types of PMOs and Their Relevance to Innovation
A
A supportive PMO acts as a resource hub, offering guidance, best practices, and tools to project teams without imposing strict controls. This type of
A controlling PMO enforces standardized processes and
A directive PMO takes a hands-on approach, directly managing projects and making key decisions with project teams. This model is best suited for organizations where projects are highly complex or require strict oversight. While a directive PMO or enterprise PMO can ensure alignment with strategic objectives, it may restrict the autonomy that innovation projects often require.
For organizations aiming to foster innovation, a supportive PMO is typically the most effective. It strikes a balance between providing structure and allowing the freedom necessary for creative exploration. By adapting its level of involvement based on project needs and implementing

How Can a Project Management Office (PMO) Support Innovation?
A PMO that supports innovation, balances structure, and flexibility. Rather than applying the same process to every project, it adapts support based on the nature of the work. When done well, the PMO becomes a trusted advisor, helping teams test and scale ideas with confidence. The PMO also helps foster collaboration among teams, enabling them to connect, share knowledge, and work together to support innovation and project and program success.
Aligning Innovation with Strategy
The PMO collaborates with leadership to connect innovation initiatives with business goals. It ensures the development of ideas to support organizational direction, using strategic themes and selection criteria. The PMO also ensures that innovation initiatives are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives so that every project contributes to advancing the broader goals of the organization.
What this looks like in practice:
- The PMO collaborates with leadership to define themes (e.g., digital transformation, customer experience, cost efficiency) and helps teams assess how their ideas contribute to these goals.
- It aligns teams and projects with strategic themes and the organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring innovation efforts focus on delivering business value.
- It tracks how innovation projects support the larger strategy and reports back to leadership using a portfolio view.
Creating Space for Exploration
By managing a mixed portfolio that includes exploratory work, the PMO helps organizations manage risk and pace while making room for experimentation. The PMO also plays a key role in portfolio management, ensuring a balanced approach to innovation and core projects by aligning initiatives with the overall business strategy.
What this looks like in practice:
The PMO introduces lean canvases, rapid planning templates, and pilot tracks that are easier to manage than traditional project setups.
It supports teams with short sprints, minimal upfront documentation, and clearly defined learning goals rather than fixed outcomes, while also supporting effective resource allocation across exploratory and traditional projects.
Supporting Adaptive Methods
Whether through Agile, Lean, or hybrid approaches, a PMO can help teams apply flexible methods while maintaining relevant structure. Selecting a suitable
What this looks like in practice:
The PMO helps teams structure work into sprints, define minimum viable products, and adapt plans based on ongoing feedback. Adaptive methods are particularly valuable for managing complex projects with high uncertainty and establishing the structure to handle intricate requirements.
It also ensures Agile practices are consistent across teams while allowing the flexibility required for creative problem-solving.
Enabling Collaboration Across Teams
Innovation thrives on perspective. The PMO develops routines and tools that enable teams across functions to collaborate, thereby reducing delays and misunderstandings. The PMO team plays a crucial role in facilitating cross-functional collaboration, ensuring alignment, and effective project execution.
What this looks like in practice:
The PMO organizes cross-functional steering groups, sets up shared communication platforms, and resolves conflicting resource demands. Effective task management helps reduce delays and improve coordination among teams.
It creates visibility into project overlaps and makes coordination part of the standard way of working.
Encouraging Learning and Continuous Improvement
The PMO treats each project as a source of learning, including analyzing project failures. Insights are collected, shared, and utilized to adjust future efforts, reinforcing a culture of improvement. The PMO also supports training programs to enhance
What this looks like in practice:
Teams are encouraged to reflect on what went right or wrong, using debrief forms or storytelling sessions.
The PMO compiles these insights into internal libraries, reference decks, or retrospectives that benefit the next round of ideas. Sharing these lessons learned contributes to the ongoing development of
Providing Tools and Structure Without Overhead
Instead of requiring complex documentation, the PMO offers simple templates and checklists that support progress tracking, early evaluation, and transparent communication. Essential PMO tools play a crucial role in supporting innovation projects by enabling efficient collaboration, resource management, and portfolio oversight.
What this looks like in practice:
Innovation projects are tagged separately in the portfolio but reviewed alongside other efforts.
It helps leaders make informed decisions about resource allocation, whether for improvement, optimization, or entirely new initiatives. Effective cash flow management and progress tracking facilitate transparent communication and decision-making.

Reasons You Need to Know How a Project Management Office Supports Innovation in Organizations
Innovation is no longer optional. Organizations that wait too long to change often lose ground. A PMO helps integrate innovation into project systems so that ideas don’t stall or stray. By ensuring alignment with organizational goals and providing ongoing support, the PMO improves project outcomes and helps deliver consistent value.
- Connects ideas to business goals.
- Encourages testing within manageable boundaries.
- Builds learning into how teams work.
- Balances core work with exploration.
- Supports timely decision-making.
- It prevents innovation from getting lost in the backlog.
- Encourages teamwork across roles.
- Tracks what’s working and what isn’t.
- Prepares teams for changing conditions.
- Let innovation be repeatable and visible.
A
Supportive PMO practices, such as providing resources and training, can significantly increase project success rates by enabling teams to implement best practices and adapt to challenges. It helps prevent promising efforts from being abandoned due to a lack of support or unclear priorities. It also strengthens collaboration by encouraging teams from different departments to work together and share insights. Over time, the PMO turns innovation into a routine part of project planning, tracking what works and what does not, and adapting accordingly.
Example 1: A software company’s PMO introduces a lightweight framework for early-stage ideas, helping product teams test new features in limited user segments. It enables them to learn quickly and improve their roadmap decisions without impacting ongoing releases.
Example 2: In a logistics company, the PMO sets up a shared review process for innovation proposals. By aligning them with strategic goals, leadership can prioritize the ideas that help reduce delivery time and improve sustainability rather than spreading resources thin across unrelated efforts.

Laying the Foundation: Setting Up a PMO for Innovation
Establishing a
Analyze the Situation: Assessing Organizational Readiness
The first step in setting up a PMO for innovation is to evaluate the organization’s current state. It means assessing
A thorough analysis helps pinpoint gaps in
Design the Plan: Tailoring the PMO for Innovation Goals
Once readiness is established, the next step is to design a PMO plan that supports innovation. It involves customizing the PMO’s structure, processes, and
Setting clear metrics for innovation success is also crucial. The PMO should work with leadership to ensure that innovation projects are prioritized and resourced in line with strategic objectives. By embedding mechanisms for regular monitoring and evaluation, the PMO can adapt its approach as the organization’s needs evolve, ensuring continuous support for innovation.
Implement the Plan: Launching and Embedding Innovative Practices
With a tailored plan in place, the final step is implementation. The PMO should actively support project teams and
Embedding innovative practices into the organization’s activities helps experimentation and creativity. The PMO ensures innovation projects align with strategic objectives, are delivered on time, and meet quality standards. By continuously monitoring outcomes and refining its approach, the PMO helps the organization sustain a competitive edge through ongoing innovation.

Step-by-Step Instructions for Driving Innovation
A PMO can guide innovation from idea to impact by creating a flexible path that fits within the organizational structure. It defines success metrics for innovation projects, ensuring measurable criteria are in place to evaluate progress and value. Here are five key steps:
Clarify the Purpose of the PMO in Supporting Innovation
Make it clear how the PMO will support the development of ideas. It might include offering tools, shaping early proposals, or advising on pilot funding.
Before a PMO can support innovation, it needs a clear mandate. That means defining how it will be involved in idea generation, evaluation, and delivery. Will it advise teams during experimentation? Manage funding requests for prototypes. Provide oversight for innovation pilots? The PMO manager plays a key leadership role in guiding these innovation initiatives, overseeing project quality, facilitating planning, and collaborating with stakeholders to ensure project delivery.
This clarity should be documented and shared across the organization. Without it, teams may not know whether they can approach the PMO for help with early-stage ideas or whether the PMO only steps in during execution. A purpose-aligned PMO also avoids duplicating efforts with innovation labs, R&D units, or digital strategy teams.
- Create a short statement describing the innovation role of PMOs.
- Communicate this role during onboarding, planning sessions, and executive briefings.
- Identify the boundary point where idea generation ends and structured
project management begins. - PMO managers are responsible for communicating the role of PMOs across the organization, ensuring all teams understand how to engage with the PMO for innovation support.
Introduce Lightweight Processes for Early-Stage Ideas
Simplify the process for new concepts. Offer tools for framing opportunities, quick evaluation, and first-round testing without extensive approvals.
Innovation often starts with incomplete thoughts and high uncertainty. Traditional project protocols such as detailed timelines, business cases, and rigid scopes can slow or even discourage early experimentation.
To avoid this, the PMO should develop streamlined workflows specifically for early-stage initiatives.
The PMO can standardize processes for early-stage innovation, ensuring that teams follow consistent procedures to reduce errors and improve communication. These might include one-page idea canvases, informal checkpoints instead of formal reviews, or short-term exploratory sprints.
- Develop templates tailored to early-stage concepts (e.g., opportunity brief, test plan).
- Offer guidance on how teams can frame an idea for discussion without needing project plans.
- Creates a fast-track review process for proposals that need limited investment to test and clarify whether the PMO will directly manage projects or provide guidance for early-stage initiatives.
Use Portfolio Reviews to Make Room for Innovation
Dedicate part of the project portfolio to exploratory efforts. Review them regularly using strategic fit and learning progress as criteria.
Innovation needs capacity in budget, people, or time. The PMO can work with leadership to allocate space in the project portfolio for exploration.
Project portfolio management plays a key role in supporting innovation by providing strategic oversight, prioritizing projects, and ensuring resources are allocated effectively to exploratory initiatives. It signals that experimentation is not tolerated but actively supported.
During portfolio reviews, the PMO can help compare exploratory projects using nontraditional metrics such as learning potential, alignment with long-term goals, or scenario modeling.
- Dedicate a percentage of the project budget to innovation or pilot efforts.
- Include innovation as a distinct category in portfolio dashboards.
- Support leaders in balancing known priorities with emerging opportunities.
- Portfolio managers oversee the balance between innovation and core projects, ensuring strategic alignment and optimal allocation.
Track and Share Lessons Learned Across Innovation Projects
Treat projects as experiments. Capture the ideas and experiences, and then share those insights across teams. Evaluating each project’s performance helps inform future innovation and guides better decision-making.
A failed experiment that provides information can be more valuable than a successful one that adds little insight.
The PMO can support learning by collecting and sharing outcomes, both technical and procedural. It helps future teams build on previous work rather than repeat mistakes.
- Create a simple knowledge capture form for teams to fill out after experiments.
- Host periodic learning sessions or retrospectives focused on innovation.
- Maintain a searchable repository of reusable insights, templates, and outcomes.
- Utilize key performance indicators to track and communicate the results of innovation projects.
Adjust Oversight Based on Project Type and Maturity
Not every effort needs the same level of oversight. Match guidance and tracking to the level of uncertainty and complexity.
Different innovation projects require different types of support. Early ideas might require coaching and light tracking, and advanced pilots involving customers or revenue may need more detailed governance. Risk management is essential in determining the appropriate level of oversight, ensuring that potential issues are identified and addressed early.
The PMO should tailor its involvement based on the risk, scope, and readiness of each project. It avoids burdening teams with unnecessary oversight while still maintaining accountability.
- Define project categories (e.g., early-stage idea, pilot, scale-up) with matching levels of PMO involvement.
- Tailor PMO involvement based on the stage of the project lifecycle, increasing oversight and risk management as projects mature.
- Utilize adjustable reporting tools such as lightweight dashboards for projects and status reports.
- Offer optional PMO coaching or checkpoints rather than mandatory reviews for lower-maturity efforts.

Considerations for Successfully Establishing a Project Management Office Supporting Innovation
When launching or reshaping a PMO, start by assessing the organization’s culture, risk tolerance, and project maturity. A rigid structure can discourage creative work, while an unstructured one may not support follow-through. Additionally, consider establishing a portfolio management office to provide broader oversight and ensure strategic alignment across multiple projects and programs.
Also, consider how the PMO is perceived. Rather than enforcing compliance, aim to act as a partner who helps teams shape ideas, understand expectations, and share progress.
Adaptability is essential. The PMO’s role should evolve in tandem with project practices and innovation maturity, adjusting tools and support as needed. As the organization matures, the PMO may have greater responsibilities in portfolio management, supporting enterprise-level prioritization and decision-making.

Taking It to the Next Level: Strategic Projects
Once a PMO has created a stable environment for managing both traditional and innovative projects, it can begin to evolve into a strategic partner within the organization. At this level, the PMO monitors delivery and actively shapes projects, resource allocation, and how outcomes support long-term goals. An enterprise PMO, in particular, drives organization-wide innovation by aligning projects with business objectives and standardizing practices across all departments.
This shift means becoming more than a delivery hub. The PMO influences organizational priorities, portfolio decisions, and transformation programs. It also contributes to strategic planning by ensuring that project selection and execution align with the organizational goals, supporting long-term value creation.
Below are three examples of how a PMO can operate at this more strategic level:
Guiding Enterprise-Wide Digital Transformation
A large manufacturing company is establishing factory capabilities by introducing automation, IoT sensors, and predictive analytics into its production lines.
Strategic Role of PMOs:
- Coordinates digital projects across IT, operations, and engineering.
- Sets up a strategic roadmap for transformation that aligns with corporate goals, such as efficiency and sustainability.
- Tracks dependencies between initiatives and flags risks tied to integration or regulatory concerns.
- Advises leadership on readiness for scale, change management plans, and training needs across departments.
- Leverages guidance from the
Project Management Institute to ensure the adoption of best practices and alignment with recognizedproject management standards.
The PMO helps ensure that digital efforts are not undertaken in silos, but rather as part of a cohesive modernization strategy. Adherence to

Wrapping Up: Strategic Alignment
A
When the PMO welcomes experimentation and guides exploration without slowing progress, it contributes to projects and better outcomes. In the end, innovation becomes not an event but a system supported by clarity, collaboration, and intent.
References
Project Management Institute. (2023). PMBOK® Guide – Seventh edition: A guide to the
Retrieved from https://www.pmi.org/pmbok-guide-standards/foundational/pmbok
Project Management Journal. (2020). The role of the
Walker, D. (2025, May). How award-winning PMOs drive business transformation.
Retrieved from https://www.pmi.org/blog/how-award-winning-pmos-drive-business-transformation

